As a Cloud Management Solution Specialist, i often get questions related to resource placement in Aria Automation.
I most recently had a customer ask me, “how can i get Aria Automation to deploy VMs on the datastore cluster that has the most free space available, and chose compute placement based on the chosen datastore cluster”.
This specific customer had a large amount of datastore clusters and their objective was to balance space usage across all those different datastore clusters.
In this example, i will attempt to explain how an external action can be used to run some business logic in order to influence the placement of resources. In this case specifically, the external action will discover and identify the datastore clusters that have the most free space available. Obviously, this is just an example and the same logic could be used and applied for many use cases.
First, we need to talk about tags. Constraint and Capability tags:
Capability Tags : In Automation Assembler, capability tags enable you to define deployment capabilities for infrastructure components. Along with constraints, they function as the basis of placement logic in VMware Aria Automation.
Tags added to projects and cloud templates function as constraint tags when they are used to match capability tags on infrastructure resources, profiles, and cloud zones. In the case of cloud templates, Automation Assembler uses this matching functionality to allocate resources for deployments, in our use case, storage and storage profiles.
So the strategy is the following:
- Tag all datastore clusters (or datastores if not using clusters) with a capability tag with format datastoreName:datastore_name.
- Create an Orchestrator action that fetches all available datastores/clusters in Automation and returns the name in the format of a tag to be used in the cloud template.
- Create a cloud template that uses an external action (Orchestrator action) to return the datastore cluster with the most free space and apply this as a storage constraint.
Tagging datastores and datastore clusters
In Aria Automation Assembler, Infrastructure/Resources/Storage
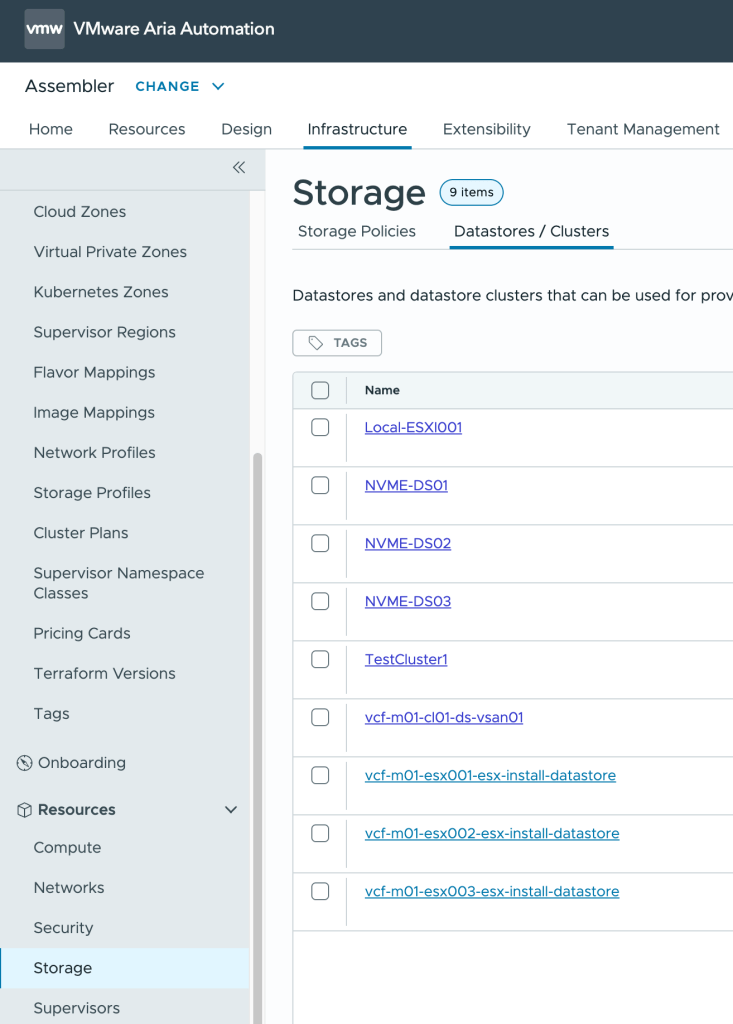
Select the datastores/clusters you want to consume and tag them with datastoreName:datastore_name
The tag prefix datastoreName: is an example only and we will see in the Orchestrator action that we can use the input parameter tagPrefix to specify this tag prefix. The important part is that the name of the datastore be the tag value.
To add a tag, select the datastore then click TAGS button and enter the tag key:value (datastoreName:datastore_name)
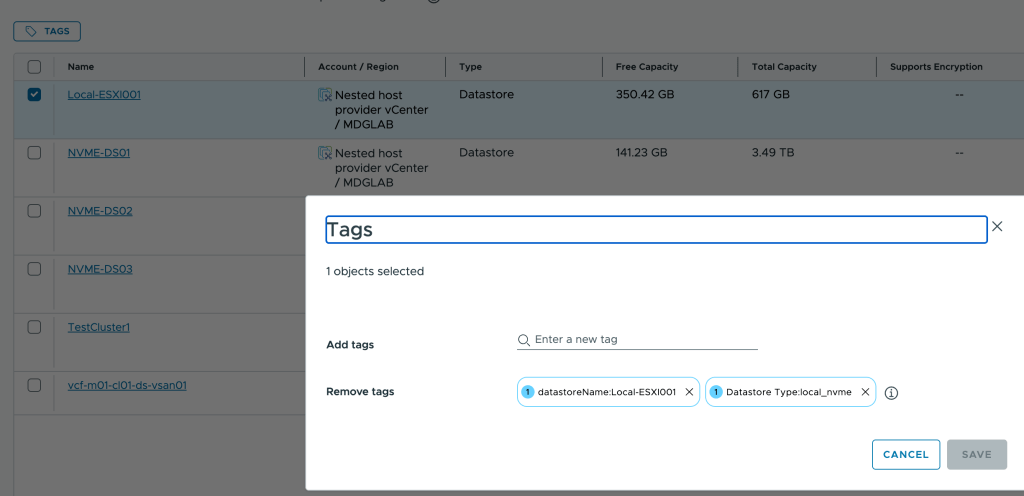
Example of my tagged datastores/clusters
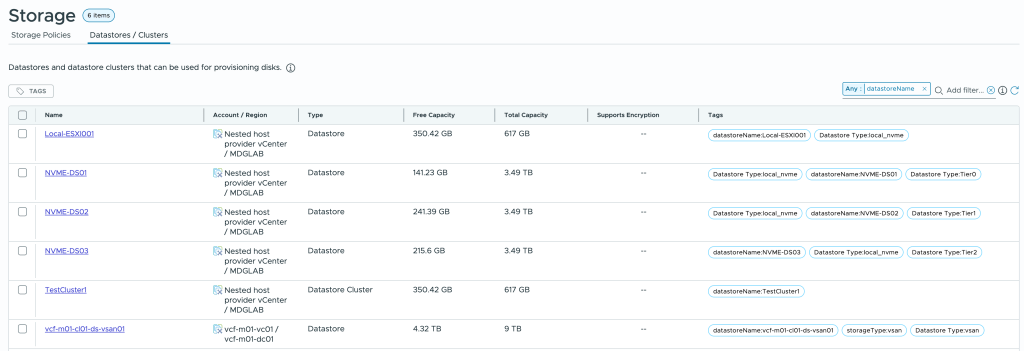
Create an Orchestrator action to return the datastore/cluster with the most free space remaining
If you have never configured actions in Aria Orchestrator, check this link for guidance.
The action we are creating will have 4 inputs and 1 output and is called getDatastoreWithMostFreeSpace:
Output is a string in the format : tagPrefix:datastore_name
Inputs are all optional (but as a minimum, prefix should be used if you want to use the output as a tag)
tagPrefix : prefixes the datastore name returned with your value. typical use “datastoreName:”
storageTypeFilter: if you want to filter on the datastore type, select NFS, VMFS or StoragePod for a datastore cluster.
storageNameFilter: if you want to return a list of datastores that match a specific pattern or exclude some datastores
nRecordsToReturn: by default will only check the first 250 datastores that match the filters, if you have more you can change this value
var vraHost = VraHostManager.findHostsByType("vra-onprem")[0];
var vraRestClient = vraHost.createRestClient();
// storageTypeFilter can be VMFS, NFS or StoragePod for datastore clusters
if (!storageTypeFilter) { storageTypeFilter = '*'; }
// storageNameFilter can be an expressions like "Prod-Cluster*"
if (!storageNameFilter) { storageNameFilter = '*' }
// nRecordsToReturn can be any number, this sets the max number of records to return
if (!nRecordsToReturn) { nRecordsToReturn = 250 }
var url = "/iaas/api/fabric-vsphere-datastores/?$filter=type%20eq%20"+storageTypeFilter+"%20and%20name%20eq%20"+storageNameFilter+"&$top="+nRecordsToReturn;
var request = vraRestClient.createRequest("GET", url, "");
var mostFreeSpaceDatastoreSize = 0;
var mostFreeSpaceDatastoreName;
var requestResponse = vraRestClient.execute(request);
if(requestResponse.statusCode != 200)
{
System.log("Error fetching datastore information!");
throw "Error: " + requestResponse.contentAsString;
}
jsonResponse = JSON.parse(requestResponse.contentAsString);
for each(datastore in jsonResponse.content) {
System.log("Datastore is " + datastore.name + " of type " + datastore.type + " with free space of " + datastore.freeSizeGB + " GB")
if (datastore.freeSizeGB > mostFreeSpaceDatastoreSize) {
mostFreeSpaceDatastoreSize = datastore.freeSizeGB;
mostFreeSpaceDatastoreName = datastore.name;
}
}
System.log("Number of returned records is : " + jsonResponse.numberOfElements + "/" + jsonResponse.totalElements)
// tagPrefix can be used to return the name of the datastore in a tag format for use as a constraint in a cloud template. It is optional
// ie tagPrefix example would be datastoreName: , this would return a datastore name with the prefixed value ie datastoreName:DSCluster01
return tagPrefix+mostFreeSpaceDatastoreName;The steps in the action are the following:
- Connect to the embedded vRA and create a rest client
- Parse inputs and build the URL for the API call to Automation to get the list of known datastores
- Execute the API call and validate response
- Loop thru the list of datastores and get the name of the one with the most free space.
- Add a prefix to the datastore name (if none provided, will simply be null)
- Return the prefix+datastore name
So, assuming we used “datastoreName:” as a prefix and the datastore name with the most free space is “Datastore01” then the returned value from this action would be “datastoreName:Datastore01”.
This is the perfect tag format that we can use in our cloud template as a storage constraint.
Test the action before continuing to the next step to make sure it is returning the expected results.
Adapting the cloud template to call our external action to provide the required constraint tag
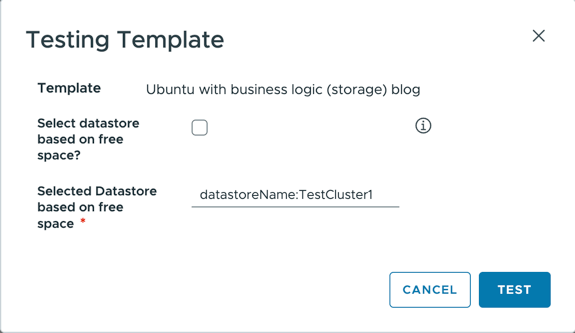
Here is a very simple cloud template that deploys an ubuntu VM image.
It has 2 inputs:
- pickDsWithFreeSpaceFirst : bool
- This is to give the option of using or not the datastore with the most free space.
- lessUsedDatastore: string
- value returned from our Orchestrator action, basically a constraint tag in format datastoreName:datastore_name
If the user checks the checkbox, the datastore used to deploy the VM will be the one that has the most free space.
If the checkbox is not checked, then the datastore used will be one that matches the constraint “datastoreType:vsan”. We will see later bellow how we are setting the default storage constraint to be “datastoreType:vsan”.
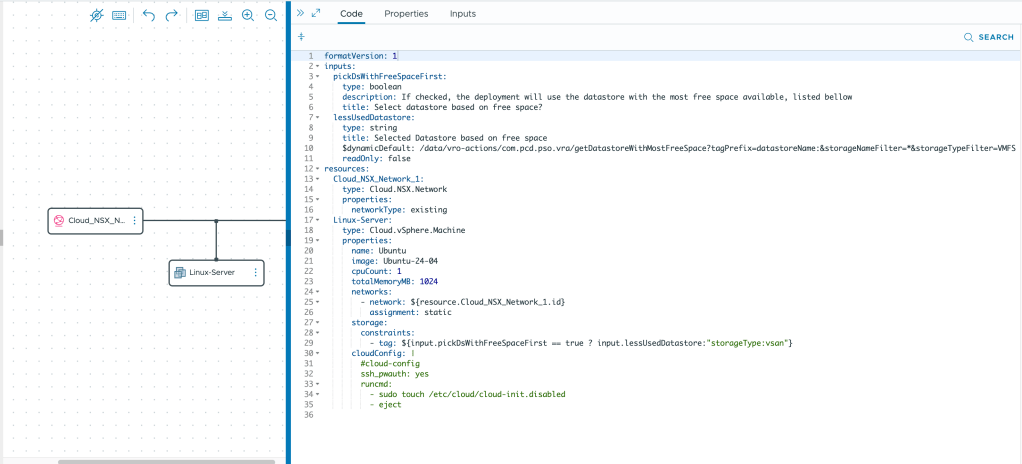
There are 2 critical constructs in this cloud template, lets analyze them :
lessUsedDatastore:
type: string
title: Selected Datastore based on free space
$dynamicDefault: /data/vro-actions/com.pcd.pso.vra/getDatastoreWithMostFreeSpace?tagPrefix=datastoreName:&storageNameFilter=*&storageTypeFilter=StoragePod&nRecordsToReturn=250The first is about the ability to have an input’s value to be provided by an external action.
The $dynamicDefault option provides this capability. The value must be an Aria Orchestrator action with any required parameters. In my case, the action is getDatastoreWithMostFreeSpace in the com.pcd.pso.vra module and the 3 parameters mentioned in the action definition.
The action returns as string thus the input has to match the type (string).
If you are not sure about the syntax, you can use the designer UI to pick the action and setup the parameters.
First, switch from the Code tab to the Inputs tab:
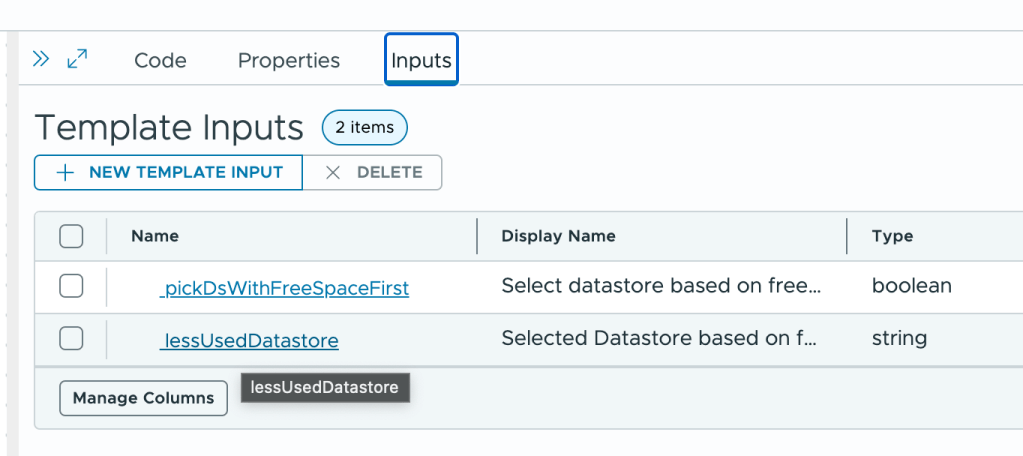
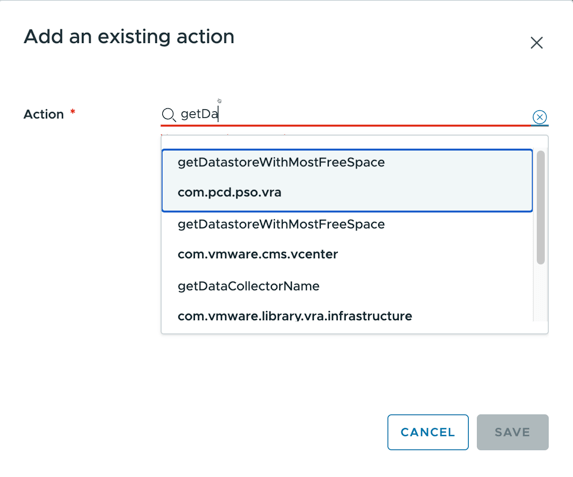
Choose the input to configure and select External source and click on select to chose the action to run.
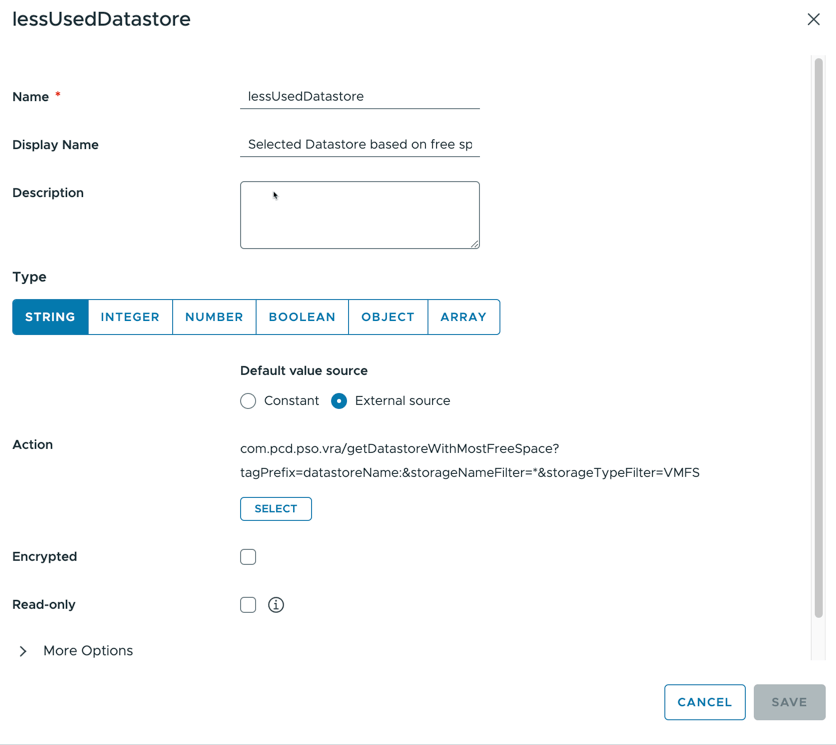
Start typing the name until you see your action and select it:
At this point, you will be able to see the available parameters of the action and enter static values or bind them to other items in the cloud template:
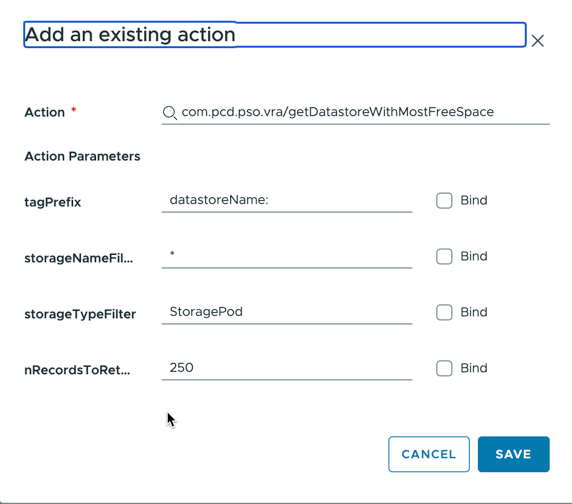
Click save and that input is configured to automatically get its value from the selected action anytime the form is refreshed.
This completes the input setup, now to configuring the storage constraint:
Storage constraint is simple, provide a valid tag. In my example, that tag will be coming from a logical expression:
storage:
constraints:
- tag: ${input.pickDsWithFreeSpaceFirst == true ? input.lessUsedDatastore:"storageType:vsan"}If the user selects the checkbox pickDsWithFreeSpaceFirst, then the expression resolves to true and the input value of lessUsedDatastore is used as the constraint tag. Obviously, the content of lessUsedDatastore must have a matching capability tag so that its matched in the allocation phase.
Else, the constraint tag is set to the static value of “storageType:vsan“, which in my lab, deploys to my default vSAN datastore.
Implementing this should enable you to influence storage placement based on disk space usage.
As for compute, in general, datastore clusters are mapped 1:1 with compute clusters. So the chosen compute cluster will be whatever that datastore cluster is attached to.


Leave a comment